The Four Stages of Data Modernization for Digital Transformation
Digital Transformation (DX) is crucial to every business, from small-scale enterprises to medium-sized businesses to multinational corporations. Our world is becoming increasingly digital, and how a company carries out its DX initiatives determines its competitiveness and relevance today.
Since the term ‘digital transformation’ means different things to different businesses, it is hard to define it. However, in general terms, digital transformation is the integration of digital technology into every key area of a business that impacts the fundamentals of its operations and its value delivery to customers.
Beyond that, DX is a cultural reform in which enterprises continually challenge the status quo and get comfortable with trials and errors. This also means that the business organizations should walk away from legacy business operations on which the company was built and embrace new business practices.
What Is Data Modernization?
In today’s digital Information Age, unimaginable volumes of data get generated every second from countless devices and sources in structured and unstructured formats. The mixture of structured data (such as documents and spreadsheets) and unstructured data (blog posts, videos, and social media comments) brings storage and data processing challenges.
Unfortunately, most organizations struggle to put this enormous data into effective use without realizing two essential things. First, their legacy data architectures stand in the way of generating deep insights for effective decision-making. Second, data modernization is the key to unlocking the limitless potential of data processing.
Data modernization helps enterprises move siloed data from legacy databases to modernized cloud-based databases or data lakes. Legacy systems have several inefficiencies, complexities, and bottlenecks. An enterprise that embraces data modernization eliminates those obstacles and turns into an agile one. So, data modernization is the foundation of digital transformation in an absolute sense.
The Four Stages of Data Modernization
Let’s explore the four stages of an efficient data modernization process toward successful digital transformation.
- Data Migration
Data migration is the first step of data modernization and most DX projects. Unfortunately, in most cases, the professionals complicate the process or tend to prematurely transform the data before data migration. Instead, they could have performed a lift and shift migration: a process that allows quicker data migrations and lets organizations leave legacy systems faster.
- Modernization of Data and Application
After the data has been migrated to the cloud, the data and application modernization phase commences. As it is carried out on the cloud, this phase enables a wide range of capabilities that are difficult to attain from on-premises (on-prem) systems. Some examples are real-time collaboration, easily accessible data sharing, and a more straightforward yet more informative Business Intelligence (BI) dashboard.
- Implementation of Modern Analytics
Data modernization empowers an enterprise to obtain more meaningful insights from data. And with modern analytics, an organization can learn more about their customers, identify customer behavior patterns, and make more informed decisions.
In addition, connecting multiple data sources to cloud-based modern analytics is simpler than connecting on-prem databases to similar data sources. Cloud-based data pipelines are easier to build and smoothly navigate through problems such as data gravity that on-prem databases fail to deal with.
- Apply Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Innovation
Businesses have been using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to overcome several business challenges in recent years. The last stage of data modernization is to unlock the innovation potential of AI and ML.
Some AI/ML use cases include manufacturing companies using AI/ML solutions to reduce waste by AI-based predictive maintenance. In addition, AI/ML solutions have been used by organizations to create customer profiles, learn more about customer behavior patterns and devise marketing strategies based on these profiles and forecasts.
Sailing Smoothly Through Data Modernization
According to a study conducted by Statista, 34% of respondents confirmed that their organization had fully implemented data modernization technology, while 50% stated that their organization is currently undergoing the implementation process.
Data modernization may still be a daunting, time-consuming process for some, even after breaking it down into four stages. It is a fact that if conducted in a standalone manner, the data modernization process wastes tons of your time and resources. The lack of continuity is one of the crucial challenges most enterprises face when implementing data modernization.
The best way to overcome this challenge is to shake hands with an Information Technology (IT) consulting firm like GoDgtl. With a focus on helping clients transform their off-line organizational activities and legacy business processes, we can help you modernize your data stack and enjoy modern and rich data experiences.
Recent Posts
In the current business world, data is the most valuable asset, and a disaster involving data loss results in several irreversible damages to an enterprise. Those damages include the loss of revenue, productivity, reputation, and even loyal customers. Disasters and their severity are hard to predict. Anyway, you can control how you respond to a disaster, and your response determines how successful your enterprise will recover from it.
The adoption of cloud computing services has been rising since the COVID-19 pandemic. A recent survey revealed that 67% of enterprises adopted cloud infrastructure by the end of 2021. Cloud computing services deliver on-demand Information Technology (IT) services from storage to applications to processing power via the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. An enterprise can access all those IT assets by paying a fee rather than owning IT infrastructure or data centers.
Here, let’s take a look at Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR) and how you can use it to your advantage.
Cloud Disaster Recovery: What is It?
CDR is a cloud-based service that quickly recovers your enterprise’s critical systems after a disaster and gives you remote access to your IT resources in a highly secure virtual ecosystem.
Conventional disaster recovery involves managing a secondary data center, a time-consuming yet expensive process. However, cloud disaster recovery has transformed the status quo by eliminating the need for traditional IT infrastructure and bringing down downtime significantly. According to the 2021 Data Protection Report by Veeam, the average downtime cost is roughly $85,000 per hour. And, the cost entirely depends on the size of the business organization – the larger the size, the larger the cost, and vice versa.
The Working of Cloud Disaster Recovery Explained
To understand the working of cloud disaster recovery, we should compare it with conventional disaster recovery. As mentioned earlier, the crucial element of conventional disaster recovery is a secondary data center where you can store all redundant copies of critical data and to which you can fail over workloads.
A conventional on-premises disaster recovery system generally includes the elements mentioned below.
- A dedicated ecosystem facilitates IT infrastructure, including maintenance, employees, and computing devices.
- Adequate server capacity for higher levels of operational performance that also allow scalability depending on the business needs.
- Internet connectivity with ample bandwidth allows remote access to the secondary data centers.
- IT network infrastructure, including firewalls, routers, and switches, are implemented to provide data availability and a reliable link between the primary and secondary data centers.
 Conventional disaster recovery is often too complex to manage and monitor. More than that, maintenance and support of a physical on-premises DR site can be costly and time-consuming. For example, the expansion of the server capacity of an on-premises data center can only be done by purchasing additional computing devices and IT resources, which demands a lot of money, time, and effort.
Conventional disaster recovery is often too complex to manage and monitor. More than that, maintenance and support of a physical on-premises DR site can be costly and time-consuming. For example, the expansion of the server capacity of an on-premises data center can only be done by purchasing additional computing devices and IT resources, which demands a lot of money, time, and effort.
The Advantages of Cloud Disaster Recovery
Cloud disaster recovery can effectively deal with most issues of conventional disaster recovery. Some of the advantages of CDR are mentioned below.
- Eliminates the need for a secondary on-premises physical site and the purchasing of additional hardware and software to carry out critical operations.
- Scalability of IT resources per the business needs
- The affordable pay-as-you-go pricing model requires you to pay only for the cloud computing services you use.
- CDR can be performed in minutes from anywhere in the world over any computing device connected to the internet.
- The backup of data across multiple geographical locations eliminates the possibility of a single point of failure. Even if one cloud-based data center fails, you can still retrieve a backup copy of your critical data.
- Cloud-based state-of-the-art IT network infrastructure ensures that the cloud services provider quickly identifies and rectifies any issues or errors. Moreover, the cloud service provider provides 24/7 support and maintenance of the cloud storage and consistent updating of hardware, software, and cybersecurity features.

Disaster recovery in the cloud is increasingly becoming a popular choice for small and medium-scale businesses looking to implement a robust business continuity strategy. With CDR, setting up a separate data center for backup is no longer required. Moreover, there is no need to install and maintain separate DR tools, which brings down costs while providing businesses access to continuous, scalable DR services.
Recent Posts
May, 2022
The digital revolution in healthcare is faster than ever, making public health all the more inclusive, efficient and sustainable. Healthcare organizations are embracing new, data-centric technologies to handle the constant strain on global healthcare systems due to several factors. Healthcare data amounts to almost 30% of the world’s total data volume, while the compound annual growth rate of healthcare data is projected to reach 36% by 2025. That’s 10% more than financial services, 6% higher than manufacturing and 11% faster than media & entertainment.
Data-driven healthcare and cloud solutions are helping healthcare professionals lower costs, provide better care and improve satisfaction. These technologies make it easier for hospitals to align business outcomes with patient outcomes by stimulating processes as well as operational efficiency. Life Sciences and pharmaceuticals have previously relied on experimental observation and costly clinical trials. Recent developments in data sciences have allowed researchers to streamline complex studies. With increasing bandwidth, networking capabilities, and processing power, healthcare information systems are improving with no end in sight. Read more to find out how data and cloud services have increased the scope of impact that quality healthcare has on our lives.
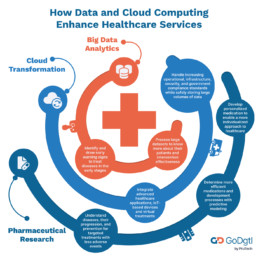
How Data and Cloud Computing Enhance Healthcare Services
Big Data Analytics
Big data is massive amounts of information generated from different sources, stored and analyzed to derive a simpler, more practical truth from the larger picture. Big data has been previously associated with supercomputers, nuclear physics and defense simulations.
Cloud-based solutions like Microsoft Azure can process datasets that are otherwise too large or complex for traditional database systems. As a result, this derivation serves as meaningful information for researchers, patients, doctors, and administrators. For example, healthcare organizations can leverage big data to predict and prepare for a future health crisis.
Big data allows healthcare professionals to drill down and know more about their patients and the effectiveness of the care they provide. Since doctors can identify and draw early warning signs, it becomes possible for them to treat diseases in the early stages. In addition, hospitals can use underutilized health records by merging data from clinics, other healthcare institutes and public health records.
Cloud Transformation
Organizations with bigger employee populations are turning to cloud healthcare solution providers to enable more affordable yet high-quality healthcare services. Cloud provides them with the flexibility, scalability and security needed to keep up with the exponential medical and digital technology advancements.
Leading healthcare organizations have already initiated value-generating cloud transformations that bring various benefits to practitioners and patients alike. Cloud-based solutions help healthcare professionals deal with the ever-increasing operational and infrastructural costs, government compliances, and security concerns. With remote storage, hospitals can access a network of servers where they can safely store large volumes of data.
Cloud offers the amount of interoperability required for advanced healthcare applications such as collaborative patient care, IoT-based devices and quality virtual treatments. For instance, Google Cloud Platform’s (GCP) healthcare data engine makes data immediately useful by providing an interoperable, longitudinal patient data record.
Pharmaceuticals and Research
Data analytics can ensure that the right patient has the right medicine at the right time. Pharmaceutical and research organizations can utilize data to understand diseases better, their progression and prevention and create safer, targeted treatments with minimal adverse events.
Predictive modeling enabled by large datasets can help determine more efficient medications and development processes. More accurate therapy trials with medicines for specific categories of the population or individuals are possible through advanced statistical analysis and better study designs. Big data applied in biomedical research can help us gain novel insights on a granular scale.
This can help with developments in personalized medication and enable a more individualized approach to healthcare. Leading industries in biomedical sciences have leveraged Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud platform for almost a decade to do more with their data.
Transform to Digital to Let Data Transform You
Today, digital transformation is not merely adopting a bunch of feature-rich software and getting your data online. There are several digital technologies and cloud-based applications to choose from. However, businesses need to go by a proven methodology and incorporate only the right solutions to reach the highest level of efficiency.
GoDgtl has partnered with the industry’s leading cloud platforms to provide healthcare organizations with the full benefits of the modern data landscape. We can help you evaluate the most suitable cloud platform and set up optimal agile processes along with robust security measures across the enterprise.
Recent Posts
April, 2022
Cloud computing facilitates storing or accessing applications, programs, and data over the internet instead of directly accessing them on your computer hard drive. The cloud icon often used to picture the Internet in flowcharts and diagrams inspired the term cloud computing.
Most of us would have already used several cloud computing services in our personal or professional lives. For example, document sharing services like Google Docs, Microsoft 365, and Dropbox; social networking sites like Facebook and Twitter; telecommunications applications like Skype; online streaming services like Netflix; Machine Learning (ML), Big Data analysis and Internet of Things (IoT) are all popular cloud computing services.
The worldwide cloud computing market is valued at roughly $369 billion in 2021 and is speculated to increase in size at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of nearly 16% from 2022 to 2030.
There are several types of cloud services. Some of the most popular ones are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). These cloud computing services can be set up in public or private cloud computing ecosystems.
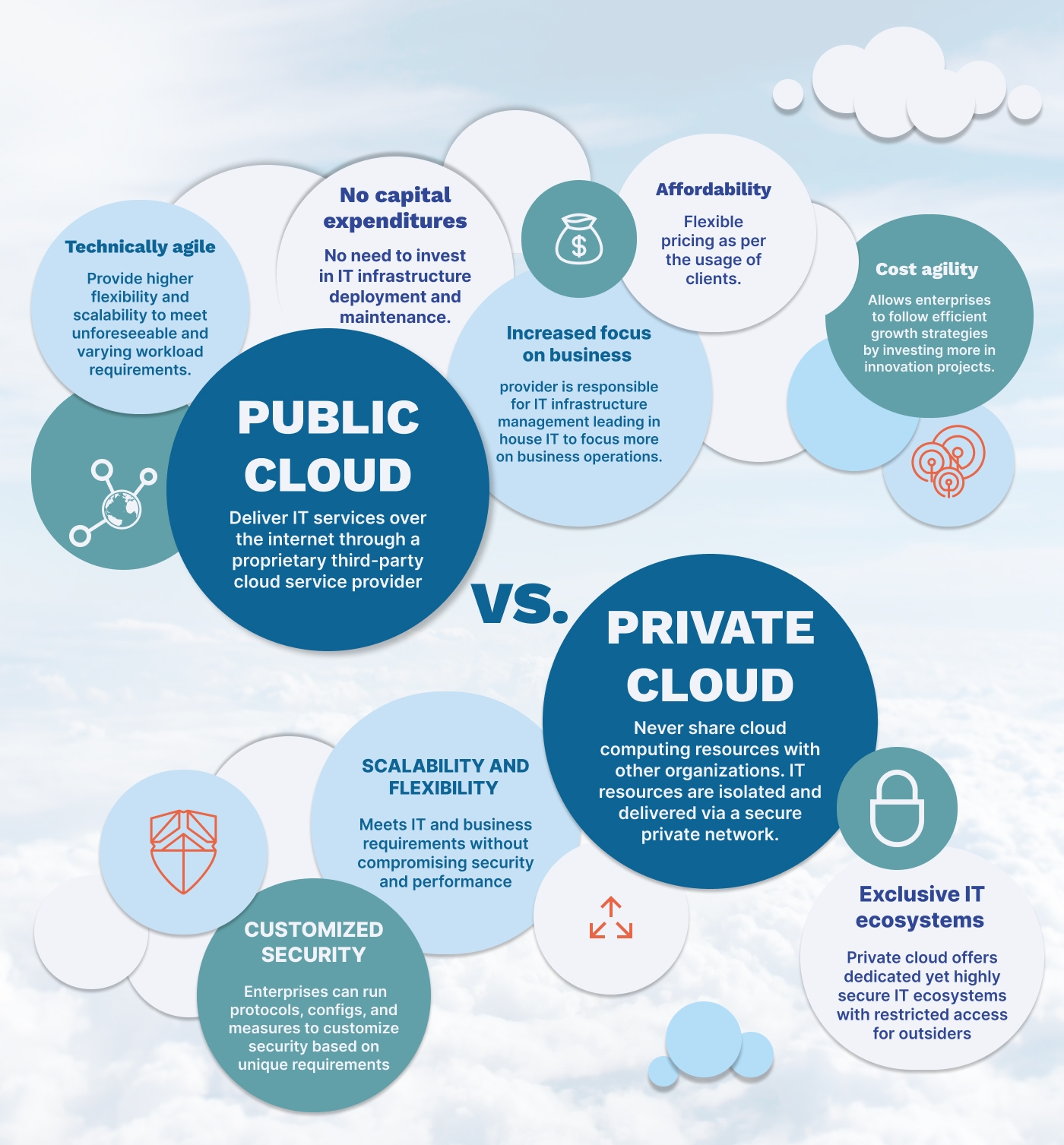
The Public Cloud
Public clouds – the most popular cloud model – deliver Information Technology (IT) services like storage and servers over the internet by a proprietary third-party cloud service provider. Every hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure in a public cloud is owned and operated by the cloud services provider. The user can access these services by managing an account using a web browser.
The unique features of public cloud services include:
- Higher levels of scalability and elasticity
- A lower subscription fee based on tiered pricing
Public cloud computing services are offered as free, freemium, or premium models, in which you are charged based on the IT resources you use. The public cloud computing services may range from standard IT services like email, applications, and storage to the enterprise-grade Operating System (OS) platform or IT infrastructure used for software development and testing.
The third-party cloud computing services provider is responsible for developing, operating, and maintaining the pool of IT resources shared between multiple users from across the network.
Public Cloud Use Cases
The public cloud computing services are best suited for the following business ecosystems.
- An enterprise with predictable IT needs like communication or collaboration services for a specific number of users.
- An enterprise in need of applications and services necessary to perform specific IT and business operations
- A business that requires additional IT resources to meet varying demands and requirements
- To meet software development and testing requirements
Benefits of Public Cloud
- No capital expenditures (CapEx): An enterprise doesn’t need to invest in IT infrastructure deployment and maintenance.
- Technically agile: It provides higher flexibility and scalability to meet unforeseeable yet varying workload requirements.
- Increased focus on business: The cloud services provider is responsible for IT infrastructure management. So, the complexities and requirements of in-house IT expertise are minimized, bringing more focus on business operations.
- Affordability: Flexible pricing as per the usage of clients.
- Cost agility: It allows enterprises to follow efficient growth strategies by investing more in innovation projects.
Pitfalls of Public Cloud
- Lesser control over cost: In higher usage, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) can also increase accordingly.
- Lower cybersecurity levels: Public cloud is the least secure cloud computing service, and it is not suitable for information-sensitive and mission-critical IT operations.
- Lower technical control: Lower visibility and control of the public cloud IT infrastructure may not meet your compliance needs.
The Private Cloud
The private cloud is a dedicated yet ‘private’ cloud computing service. An enterprise that uses a private cloud never shares its cloud computing resources with any other organization. Instead, the IT resources are isolated and delivered via a secure private network. The private cloud can be customized as per a business organization’s specific business and security needs.
Private Cloud Use Cases
The private cloud is suitable for:
- Government agencies and highly regulated industries
- An enterprise that uses sensitive data
- Businesses that require solid control and security over their workloads and IT infrastructure
- Enterprises that need advanced data center technologies for efficient and cost-effective business operations.
Benefits of Private Cloud
- Exclusive IT ecosystems: Private cloud offers dedicated yet highly secure IT ecosystems with restricted access for outsiders.
- Customized cybersecurity: Enterprises can run protocols, configurations, and measures to customize security based on unique workload requirements.
- Scalability and flexibility: Higher scalability, flexibility, and efficiency to meet unforeseeable requirements of ever-changing IT and business environments without compromising performance and security.
Pitfalls of Private Cloud
- Higher Cost: The private cloud is expensive compared to public cloud services.
- Immobility: Due to higher security measures, users with mobile devices have limited access to private cloud services.
- Lower Scalability: The private cloud infrastructure may not offer higher scalability if the cloud data center is based on on-premise IT resources.
Recent Posts
March, 2022
In today’s Digital Age, tremendous amounts of data are generated every single second from endless sources in various formats. First, there is structured data such as documents and spreadsheets, and now on the other side, there is unstructured data like emails, blog posts, videos, and even Twitter posts thrown into the vast mix of data. A recent study by Statista reveals that the total volume of data created, captured, and consumed globally reached 64.2 zettabytes in 2020. The study also predicts that by 2025, data creation worldwide is estimated to cross 180 zettabytes.
Every business organization in every shape and size all over the globe is pursuing digital transformation today. The generation of larger volumes of data together with global enterprises’ collective effort to transform themselves into digital businesses brings up storage challenges and the trouble of processing those myriad data types in vast volumes. Both these challenges put most business organizations under tremendous pressure to use a larger volume of data efficiently.
It is often legacy data architectures that stand in the way of nearly limitless opportunities to generate insights for effective business decision-making. Today’s massive surge in the volume, variety, and velocity of data baffles legacy databases, and they are bending under the heavyweight of these data challenges. Sooner or later, they may break. The only digital system that desperately needs modernizing is conventional on-premises data architecture. And the answer is data modernization.
What Is Data Modernization?
Data modernization includes extending yet retaining the value of legacy data assets, reusing the data buried in the layers of legacy databases, transforming them to updated modern data architectures, and correlating legacy data assets with the latest high-velocity data assets. It involves developing a scalable, flexible data stack, including modernizing databases without the limitations of many stages, integrations, and complexities. In other words, data modernization is simply moving data from legacy databases to modern databases. It is highly crucial for an enterprise that primarily deals with unstructured data.
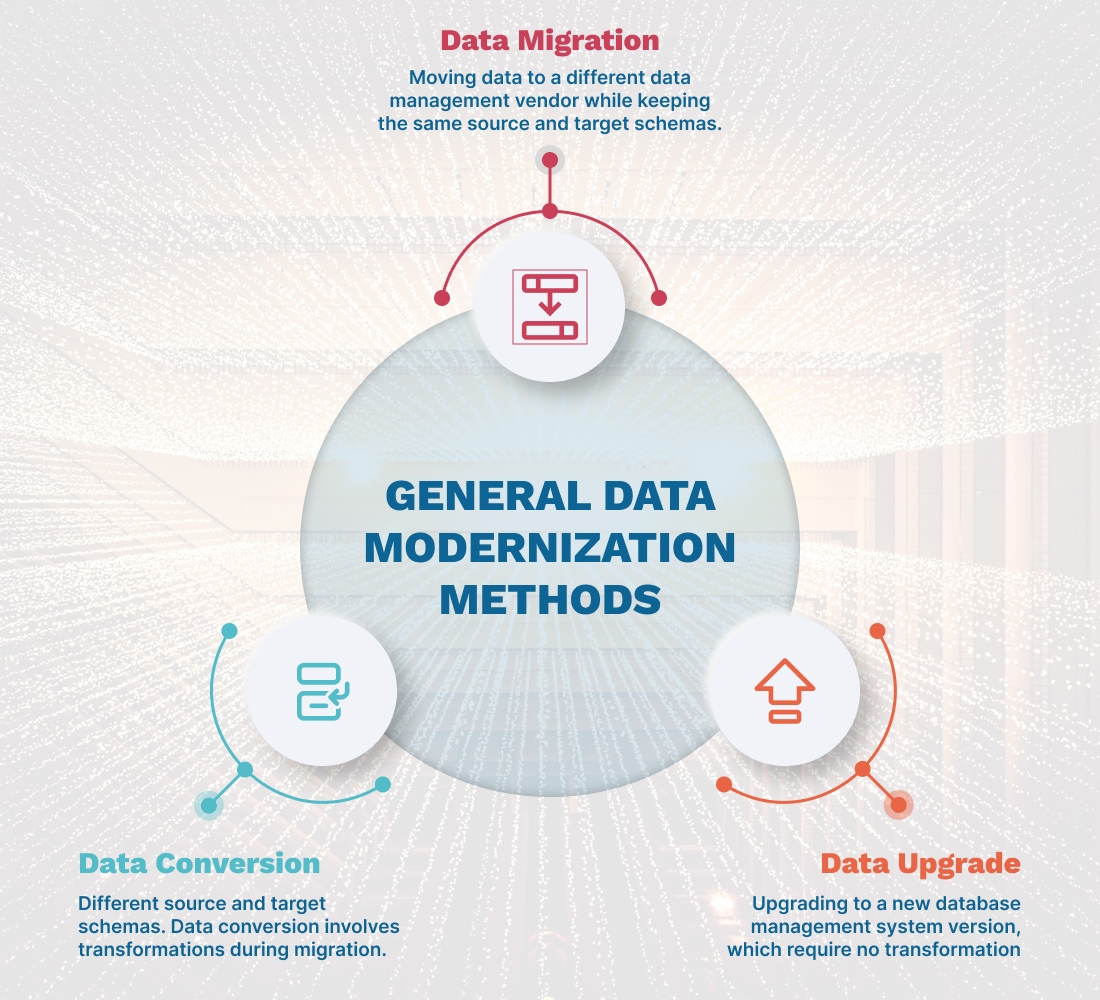
Three General Data Modernization Methods
Every business organization has its strategies and objectives. Therefore, data modernization doesn’t come with a one-size-fits-all size. Anyway, enterprises can implement three general data modernization methods depending on their business strategies and objectives.
Data Migration
This method involves moving data to a different data management vendor while the source and target schemas remain the same. Data migration includes migrating code, procedures, etc., which usually brings no significant changes to the application. In addition, an enterprise can utilize automation tools for complete data migration. For instance, moving the data from Sybase, a database management system (DBMS) vendor, to save licensing costs comes under data migration.
Data Conversion
The source and target schemas are different during this data modernization process. Data conversion involves transformations during migration. It is a typical data modernization method during re-engineering an application and modernizing a legacy application. Despite the availability of Extract Transform and Load (ETL) tools, the process is manual. For example, data movement from legacy databases like Indexed Sequential Access Method (ISAM) to Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) comes under data conversion.
Database Upgrade
This data modernization method involves upgrading to a newer version of the database management system, which requires no transformation. The deprecated code is replaced, and an enterprise can use automation tools to complete the upgrade. For instance, upgrading from SQL Server 2005 to SQL Server 2012 can be considered a data upgrade method.
 The Benefits of Data Modernization
The Benefits of Data Modernization
Here are some of the enterprise benefits of data modernization:
- It brings scalability to an enterprise to meet growing data analytics needs
- Efficient integration of new data sources to utilize data at any scale focusing on rising data volumes from multiple data sources
- Reduces the time to derive business insights. That means it provides the ability to find value in data even from streaming real-time data quickly.
- Democratize the process of data access for every business function
- Data modernization offers substantial cost benefits over traditional data management technologies.

Data modernization enables Information Technology (IT) enterprises and business leaders to attain and interpret data to anticipate market trends and improve business outcomes. As a result, a business acquires a solid competitive advantage by deriving actionable insights from enterprise data and data modernization strategies. It also allows organizations to deliver ideal Application Programming Interface (API)-driven application integrations and prompt decision-making in a dynamic business ecosystem.
Recent Posts
February, 2022
Cloud computing is no longer an emerging buzzword. Businesses across the globe have already acknowledged the potential of this technology and are increasingly moving their workloads and applications to the cloud. Given the trends, it is sufficient to say that cloud computing and usage have become the new IT standard.
However, if you dig a little deeper, you’ll see a wide array of cloud and IT leaders expecting more specific cloud trends to come up in 2022. Here are some of the top key cloud trends that are expected to arrive with the New Year:
An Increase in Hybrid Cloud Environments
According to the Flexera 2020 Report, 93% of companies worldwide operate on a multi-cloud model, while the hybrid cloud approach is embraced by 87% of them. An increase in hybrid cloud deployment is expected due to the growth in the adoption of cloud-native infrastructure. Enterprises could make use of their cloud as well as on-premise resources with cloud-native computing and workloads gathering steam that is container-based.
In the future, the usage of the cloud must be driven by specialized circumstances and specific uses rather than one-size-fits-all or default settings. Kubernetes or other such orchestration platforms and containers or other cloud-native, cloud-centric technologies can be immensely helpful in making this process feasible.
Increased Automation in Hybrid Cloud & Multi-Cloud Settings
According to predictions made by Gartner, a minimum of 95% of the total security failures taking place in the cloud in 2020 will be caused by consumers. This, in itself, shows that automation is an integral part of voiding human error and creating multilayered defense mechanisms in cloud computing.
In addition, more and more enterprises today want to find better ways to manage multiple and complex on-premise, public, and private clouds from several vendors. Therefore, it has become an important issue pushing enterprises for large-scale adoption of hybrid multi-cloud strategies that offer higher levels of flexibility and resiliency in their choice of vendors. Enterprises also want to have the option of scalability, as well as support for a broad ecosystem of services and apps. Hence, automation is likely the next go-to strategy to deal with all the complexities.
Flexibility, Security, and Reliability in Cloud Strategies
The current trends show that more and more enterprises prioritize flexible, reliable, and secure cloud strategies for their business. According to a recent AllCloud report, 27.6% of respondents said security is essential for selecting cloud vendors. Additionally, 26.3% chose reliability, and 22.4% chose flexibility as the most important criterion.
While cost seemed to be an important criterion, in the beginning, this trend is changing now, and only 13.8% of respondents listed cost as a yardstick to choose vendors, making it the fourth important aspect in cloud strategies.
Consolidation of Cloud-Native Technologies
As cloud-native ecosystems become more mature, there are changes in the technologies and tools that are a part of this ecosystem. As a result, it is likely to see more consolidation in the future with dominant players in the field, solidifying their presence and leadership in the market.
Measurement and Monitoring Will Become a Priority for IT Leaders
With the expansion of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, there is also a need for specialized IT teams to monitor diverse environments effectively and offer performance measurements. More workload is being deployed to cloud environments, giving rise to the need for having an IT team that constantly monitors and gathers metrics across the entire cloud environment. IT leaders will have to provide metrics to showcase a long-term business value offered by cloud spending.
5G-Enabled Edge Computing
Enterprises that regularly process huge amounts of data rely on the available resources of the cloud provider and the network bandwidth to complete the work at hand quickly. This is precisely where 5G-enabled computing can prove to be invaluable. This trend can help companies deliver broader bandwidth limits and higher speeds, enabling lower latency.
It is expected that 5G-enabled hybrid cloud ecosystems will take increased advantage of the available opportunities to perform edge computations and provide rapid data transfers to businesses worldwide.
Industry-Optimized Clouds
Industry-optimized clouds refer to a cloud computing system that addresses a particular industry’s specific needs and nuances. In 2022, industry-optimized clouds are expected to grow by leaps and bounds as organizations will not have to handle the complexities of their cloud architecture and infrastructure. This will go a long way to providing them with ease of administration and management.
Wrapping Up
2022 is shaping up to be the year of massive cloud computing. From businesses deploying multi-cloud strategies to embracing secure cloud solutions and advancement in encryption to protect their data, cloud computing technologies are likely to accelerate the process of digital transformation in organizations across the globe.
Recent Posts
February, 2022
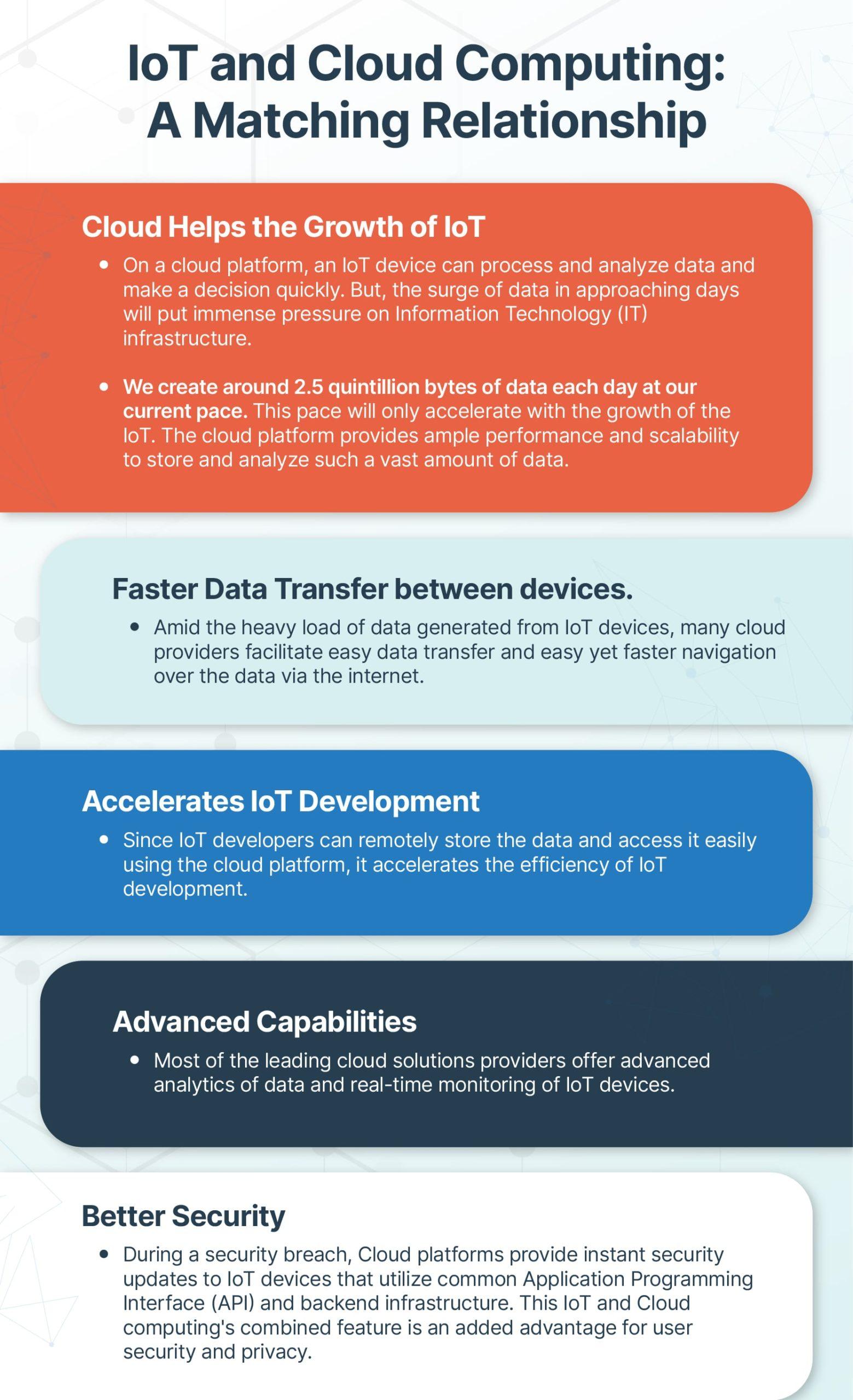
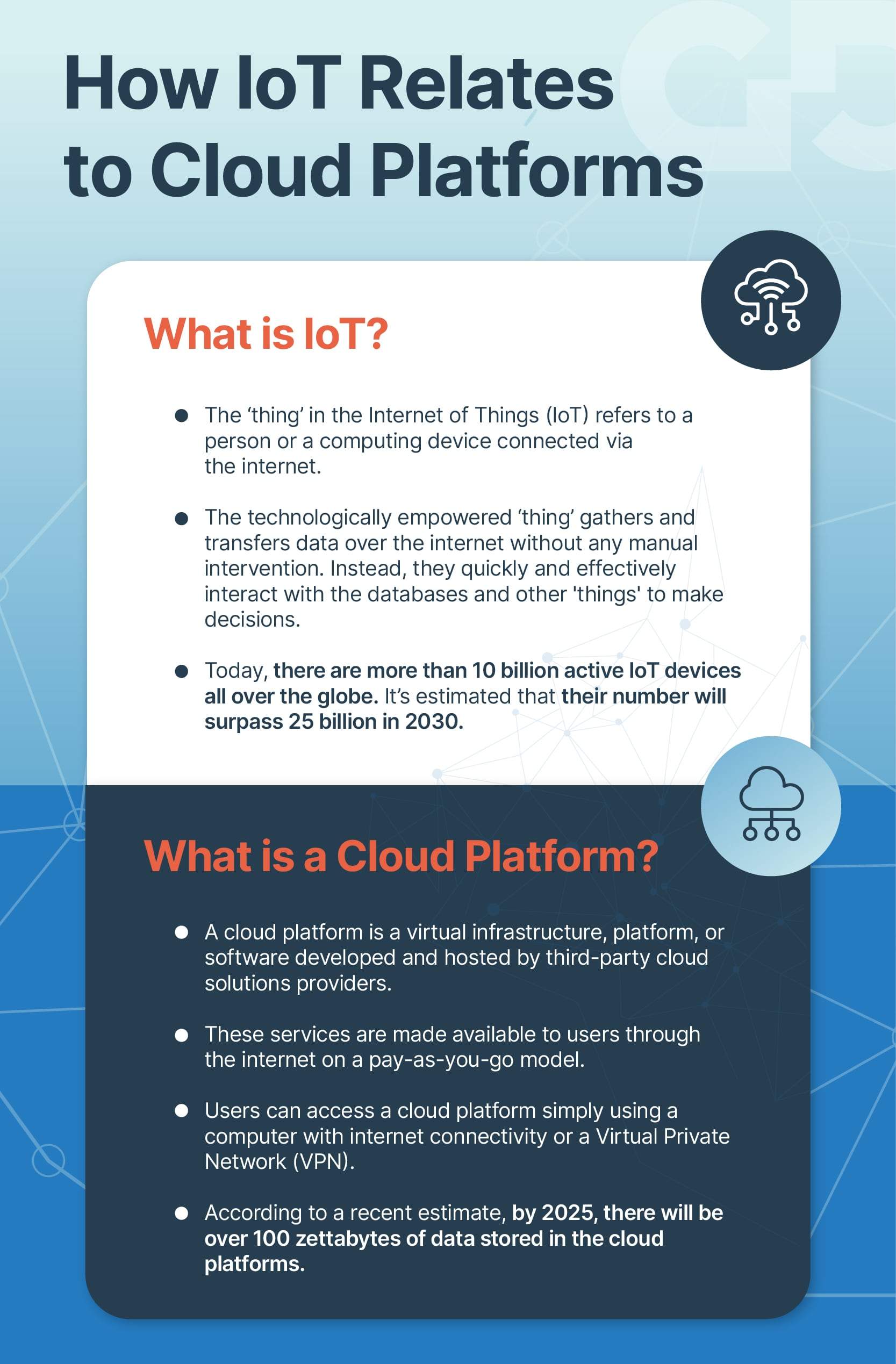
The adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) has rapidly changed today’s business world. IoT predominantly helps to capture vast volumes of data from multiple sources. However, the processes of collecting, processing, and analyzing the tremendous flow of data from countless IoT devices have turned complex.
The data-driven nature of present-day businesses requires investments in innovative technologies that can turn this complex process into a simplified yet easily comprehensible one. This is the point where the convergence of IoT and Artificial Intelligence (AI) or AIoT can play a major role in redefining how businesses and economies work.
While IoT comprises devices interacting over the internet, the Machine Learning (ML) capabilities of AI make IoT devices learn from the data they collect. AI-enabled intelligent IoT devices can simulate smart human (at times, superhuman) behavior and decision-making patterns with little or no human interference.
The Rising Trend of IoT and AI Convergence
As a prominent part of their business processes, several businesses worldwide have already embraced the combination of IoT and AI. A 2019 survey reveals that respondents that heavily use AI in their IoT operations exceeded their value expectations. Similarly, a PwC 2019 IoT survey shows that 97% of the companies that have integrated IoT with other technologies such as AI and Blockchain were able to reap the benefits through this investment.
Start-ups and large enterprises alike prefer AI technology to bring out the full potential of IoT. The major leading providers of IoT platforms like Oracle, Amazon, and Microsoft have begun incorporating AI technology into their IoT applications already.
From robotics, self-driving cars and advanced analytics to Industry 4.0 Digital Twins and smart IoT devices, AI-powered IoT is increasingly becoming important across a range of business areas. As a matter of fact, the next evolutionary step for IoT is to embrace AI and drive intelligent automation and decision-making.
How the Blend of IoT and AI Works
At its heart, IoT is all about machines with sensors implanted. These machines, over internet connectivity, transmit streams of data. All IoT devices inevitably follow five basic steps. They are:
- Create
- Communicate
- Aggregate
- Analyze
- Act
The ‘Act’ step solely depends on the ‘Analysis’ step that immediately precedes it. Therefore, the efficiency of an IoT device is determined by its Analysis step. This is the point where AI technology portrays a significant role. While IoT devices provide a multitude of data, AI offers both creativity and context to make smart actions. Therefore, businesses can make smart decisions when an unlimited stream of data delivered by IoT devices is analyzed by AI technology.
Surprising Benefits of AI-Powered IoT
Combining two disruptive technologies like AI and IoT brings a broader range of benefits for both businesses and consumers alike. Some of the most popular benefits are as follows:
Enhanced Efficiency in Enterprise Operations
ML capabilities of AI can crunch huge volumes of data from IoT devices and detect patterns that can’t be done with simple computing devices. It can also predict the enterprise operation conditions and bring solutions for ideal outcomes. Therefore, redundant and time-consuming business tasks are eliminated.

An Efficient Risk Management System
AI-Powered IoT helps businesses analyze and predict a broader set of risks and automate timely responses. It ensures efficient handling of financial loss, employee safety, and cyber-attacks.
Brings Out Innovative Products And Services
A prominent AI technology like Natural Language Processing (NLP) is getting better at letting people communicate easily with computing devices. This leads to the creation of innovative products and services yet enhances the existing ones.
Enhanced Scalability
The AI-powered IoT ecosystem analyzes and crunches the data from devices ranging from smartphones to high-end computing devices to low-end sensors. This process can make large volumes of data handy and make it easier to share across a larger network of IoT devices.
Eliminates Unpredictable Yet Expensive Downtime
In some industrial sectors like offshore oil and gas, as well as industrial manufacturing, unpredictable equipment failures can bring expensive downtime. AI-enabled IoT allows you to predict equipment breakdowns and schedule timely maintenance procedures.
Generally, IoT combined with AI technology can lead the path towards an advanced level of business solutions and user experiences. To achieve greater value from your enterprise network and to transform your business, you should undeniably integrate AI with IoT devices.
Recent Posts
February, 2022
The transformation seen in the cloud for financial services has been nothing short of phenomenal especially during the last few years. Then when the pandemic hit, cloud services were in such demand that many financial institutions were impressed with the ease with which their workforce was easily able to transition to remote office work without too many hiccups as an “underlying digital transformation” had begun years ago to help modernize the workplace.
Beyond the obvious Zoom meetings and collaboration tools flooding the market both before and during the pandemic, it was obvious that a trend towards greater reliance on cloud basedservices was underway in the financial world. These shifts were seen as advantages from the past where the big banks were at first reluctant to take the big leap into cloud, whereas now are being public about their adoption of cloud tech. For many big banks, it was a question of staying competitive and relevant in an area that has long been reluctant to any rapid changes in procedures and manners of handling sensitive customer data. The notion of putting sensitive information into a product that few were familiar with until cloud technology spread through the workforce at all levels made many in the C-suite nervous about security protocols and relied heavily on outside consultants and their internal IT security experts to educate, innovate, and manage the process of ensuring data security and privacy at all costs.
Flexibility Allows Scalability
The times have changed. Enterprise migration into the cloud has made it easier for large and small fintech firms as well as large traditional banks and other finserv institutions to streamline their workflows and innovate faster and in more seamless ways than before. The implications have been nothing short of impressive and in some cases mind boggling. According to Bloomberg, cloud adoption though in it’s early stages is still happening at a fairly robust rate, as 22% of ALL applications are now run on the cloud with more room to grow. According to the IDG Cloud Computing Study (2020), almost 55% of all financial firms and fintech companies are using multiple public clouds.
Fintechs are often rapidly growing platforms. This means they need an infrastructure that can grow with them and not put up unnecessary barriers or create challenges where there needn’t be any. Cloud technology provides the agility to scale relatively easily while saving on on-premises technology infrastructure, which can be more costly to upgrade. Even for traditional banking structures, the cloud platform delivers the capacity to adapt to branch closures while still providing services to as many people as possible. Moving infrastructure to the cloud measures accessibility, flexibility, and scalability for both fintechs and financial giants.
Another stunning figure is that these companies are dedicating 32% of their IT budgets to cloud migration and other cloud related services. It’s easy to see why this sector is finally running along with other industries in being cloud savvy. Moving to the cloud is allowing for more agile applications, more growth, more scalability and along with all that comes innovation.
Innovation
As mentioned in Bloomberg: Increasingly, businesses are developing innovations that wouldn’t necessarily be possible without the cloud: enabling fintechs to get up and running faster and offer individualized services, which has encouraged a revolution in financial services. This shift is undoubtedly broadening the competitive landscape. Many also say that agility is a major reason for seeing movement to the cloud.
Companies can now harness the resources as needed which allows for more development of applications in quicker more nimble and secure environments. As of late, even large banks are moving at a more rapid pace and sharing data like startups in the industry. Since cloud technology offers companies more options with less risk, as well as more experimentation and invention on behalf of customers, it’s possible to explore alternative data sets and spend time and capital on proprietary analysis.
New Security & Privacy Options
Despite early concerns about security and data protection, the cloud has proved reasonably secure if the right measures are taken. Zero-trust verification and encrypted data have increased cloud security in recent years. When used alongside measures such as employee education and access control, among others, the cloud proves itself no riskier than traditional IT infrastructure setups. For fintech providers, no doubt, security is at the forefront of their minds when adopting new technology, and it’s vital they ensure their systems have adequate measures in place. The financial services sector has a responsibility to safeguard the data of its customers and the cloud is enhancing the way financial businesses do this. From data encryption to zero trust verification and access control, many of the risks that traditional on-premises IT infrastructures present are being mitigated through cloud computing in financial services.
According to Bloomberg “As migrating data, storing data, and using additional services like machine learning on the cloud becomes more ubiquitous, there’s a clear and demonstrated need for organizational oversight. Many of the tools needed to keep data confidential and secure are readily available within public clouds, enabling firms to take advantage of better security than what is available on their local servers, if they plan appropriately.”


Data Management
Acquiring and working with data is a top priority, from onboarding and identity verification processes to account management, balance, checking, analyzing spending habits, etc. Data is key. Companies can use cloud technology to gather and store large quantities of data securely and make it accessible at any time. That means there’s no need to wait for an IT specialist to clock in to access vital information, providing an employee has the correct credentials. This can be done from anywhere at any time and often automatically.
Best Practices For Cloud Adoption In Finance
Working with more documentation and creating, storing and sharing a great amount of financial information make cloud adoption in banking and fintech specific. Here are the things to consider:
- Encryption and access control: Discuss encryption policies and procedures with your provider to select the technically feasible ones and properly protect the financial data you transmit.
- Compliance: Finance executives need to ask providers to demonstrate compliance certificates of the cloud service.
- Data segregation and data management: Cloud services thrive on shared resources, though financial institutions may require a combo of shared resource benefits with the increased security reached by data segregation.
- Disaster recovery plan: Reputable service providers always have it in place, and it’s important to obtain a detailed disaster recovery plan and ensure your digital infrastructure allows all that.


How GoDgtl Partners with the major cloud providers AWS, Azure, and Google
GoDgtl brings a team of experienced cloud experts who work directly with AWS, Azure, and Google to bring value and real solutions for your cloud projects. With direct access to resources and in house cloud consulting talent, GoDgtl is ready to guide you through your financial/fintech cloud journey regardless of where you are on that path. Whether it’s more knowledge-based information on cloud topics such as security, or governance and compliance or basic cloud migration aspects or even if an assessment is needed, GoDgtl can provide a roadmap for your path to project completion and success.
Sources:
https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/financial-services/cloud.html
https://www.telehouse.net/blog/the-impact-of-cloud-computing-in-fintech/
Recent Posts
December, 2021
The adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) has rapidly changed today’s business world. IoT predominantly helps to capture vast volumes of data from multiple sources. However, the processes of collecting, processing, and analyzing the tremendous flow of data from countless IoT devices have turned complex.
The data-driven nature of present-day businesses requires investments in innovative technologies that can turn this complex process into a simplified yet easily comprehensible one. This is the point where the convergence of IoT and Artificial Intelligence (AI) or AIoT can play a major role in redefining how businesses and economies work.
While IoT comprises devices interacting over the internet, the Machine Learning (ML) capabilities of AI make IoT devices learn from the data they collect. AI-enabled intelligent IoT devices can simulate smart human (at times, superhuman) behavior and decision-making patterns with little or no human interference.
The Rising Trend of IoT and AI Convergence
As a prominent part of their business processes, several businesses worldwide have already embraced the combination of IoT and AI. A 2019 survey reveals that respondents that heavily use AI in their IoT operations exceeded their value expectations. Similarly, a PwC 2019 IoT survey shows that 97% of the companies that have integrated IoT with other technologies such as AI and Blockchain were able to reap the benefits through this investment.
Start-ups and large enterprises alike prefer AI technology to bring out the full potential of IoT. The major leading providers of IoT platforms like Oracle, Amazon, and Microsoft have begun incorporating AI technology into their IoT applications already.
From robotics, self-driving cars and advanced analytics to Industry 4.0 Digital Twins and smart IoT devices, AI-powered IoT is increasingly becoming important across a range of business areas. As a matter of fact, the next evolutionary step for IoT is to embrace AI and drive intelligent automation and decision-making.

How the Blend of IoT and AI Works
At its heart, IoT is all about machines with sensors implanted. These machines, over internet connectivity, transmit streams of data. All IoT devices inevitably follow five basic steps. They are:
- Create
- Communicate
- Aggregate
- Analyze
- Act
The ‘Act’ step solely depends on the ‘Analysis’ step that immediately precedes it. Therefore, the efficiency of an IoT device is determined by its Analysis step. This is the point where AI technology portrays a significant role. While IoT devices provide a multitude of data, AI offers both creativity and context to make smart actions. Therefore, businesses can make smart decisions when an unlimited stream of data delivered by IoT devices is analyzed by AI technology.
Surprising Benefits of AI-Powered IoT
Combining two disruptive technologies like AI and IoT brings a broader range of benefits for both businesses and consumers alike. Some of the most popular benefits are as follows:
Enhanced Efficiency in Enterprise Operations
ML capabilities of AI can crunch huge volumes of data from IoT devices and detect patterns that can’t be done with simple computing devices. It can also predict the enterprise operation conditions and bring solutions for ideal outcomes. Therefore, redundant and time-consuming business tasks are eliminated.


An Efficient Risk Management System
AI-Powered IoT helps businesses analyze and predict a broader set of risks and automate timely responses. It ensures efficient handling of financial loss, employee safety, and cyber-attacks.
Brings Out Innovative Products And Services
A prominent AI technology like Natural Language Processing (NLP) is getting better at letting people communicate easily with computing devices. This leads to the creation of innovative products and services yet enhances the existing ones.
Enhanced Scalability
The AI-powered IoT ecosystem analyzes and crunches the data from devices ranging from smartphones to high-end computing devices to low-end sensors. This process can make large volumes of data handy and make it easier to share across a larger network of IoT devices.
Eliminates Unpredictable Yet Expensive Downtime
In some industrial sectors like offshore oil and gas, as well as industrial manufacturing, unpredictable equipment failures can bring expensive downtime. AI-enabled IoT allows you to predict equipment breakdowns and schedule timely maintenance procedures.
Generally, IoT combined with AI technology can lead the path towards an advanced level of business solutions and user experiences. To achieve greater value from your enterprise network and to transform your business, you should undeniably integrate AI with IoT devices.
Recent Posts
December, 2021
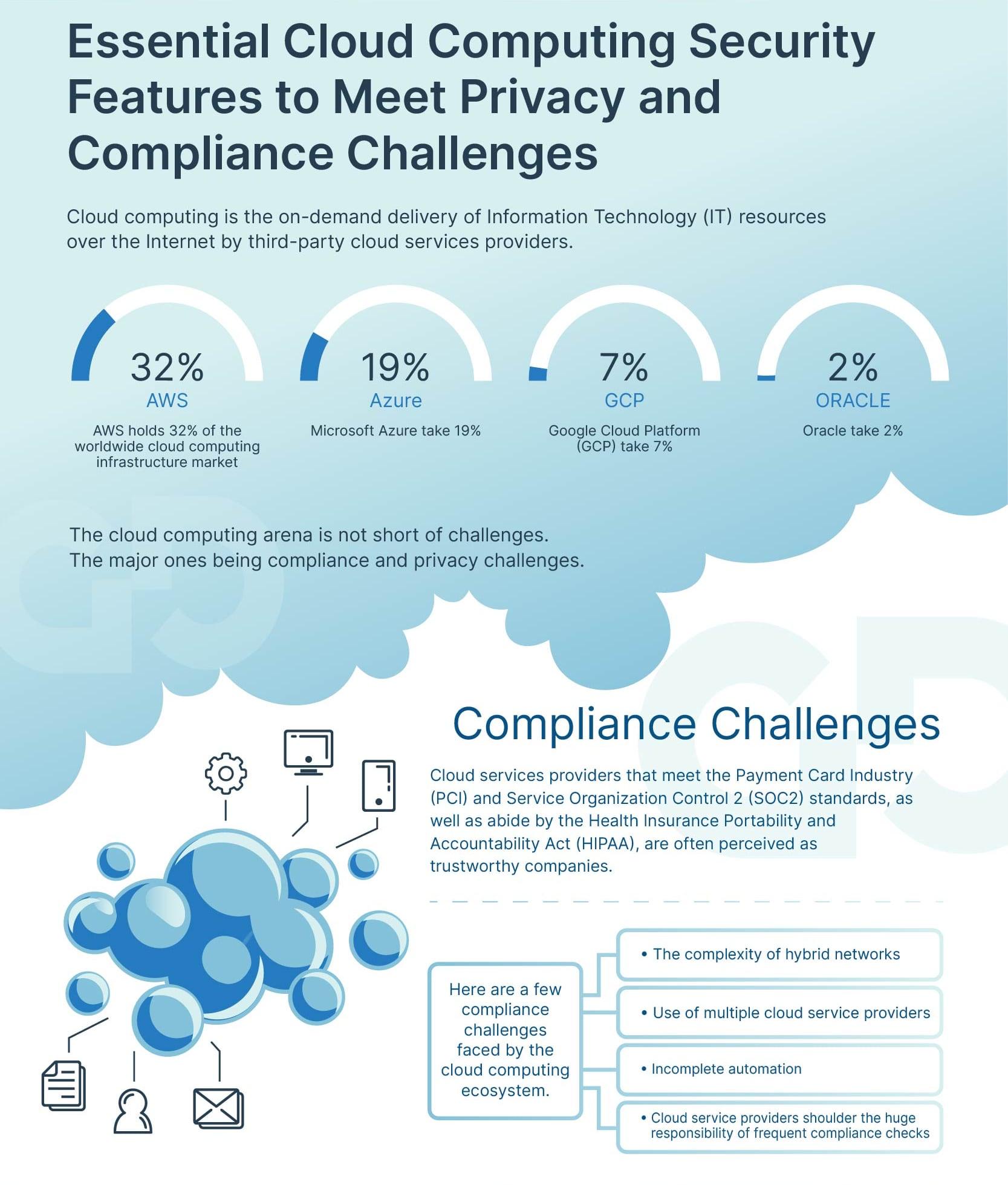
For running a business safely and securely in the cloud, you have to comply with a certain set of rules. This set of rules or policies that govern your business in the cloud environment are referred to as cloud governance. Typically, these policies share many similarities with those governing on-premise IT infrastructures.
These rules are focused on enhancing privacy, data security, and managing risks in order to secure the data and ensure the smooth operation of the application. In addition to enhancing and optimizing security and efficiency, cloud governance best practices also help economize a business’ finances by allowing it to do more with less usage of resources.
Is Changing Your Current Governance Strategy Necessary?
Since every IT business has governance protocols and strategies, you might be wondering: why must I change my existing governance framework? Is it inadequate to handle problems raised by shifting to a cloud environment?
Well, the shorter version of that answer is, Yes. That is because the traditional IT governance framework is based on using centralized tools custom-made for workers of specific departments. Although this approach is best suited for centralized tools, the cloud environment and its operations by nature are decentralized.
A cloud governance strategy allows for creating a standardized policy that can be followed by various employees and departments of the business irrespective of their roles or subdivisions.
This strategy enables every employee to share and be on an equal footing while working in the cloud environment. The cloud, like enterprise infrastructure, needs bodies that govern its environment and standardize its services and other shared infrastructure issues.
Five Pillars of Cloud Governance
The efficiency of cloud installation is definitely dependent upon the organization’s systems and procedures. However, they also impact the structure of their platform and its underlying architecture. Based on the following five pillars, one can effectively implement designs that ensure scalability.
Operational Excellence
This pillar focuses on your workload operating as desired, monitoring every process and system to yield higher business value and continuously improve them. To ensure that your workload runs effectively with governance principles, operations will have to be performed as per code, incremental development of applications, and continuous refinement of processes involved.
Reliability
Reliability focuses on ensuring that your application performs as desired and that it does so continually without encountering a complete failure. Even the most reliable applications encounter failures, but they can recover quickly to meet customer demand. This is because their workloads are distributed, and the only resources they utilize are the ones that are required for production workloads.
Performance Efficiency
Performance efficiency is all about using technical resources efficiently for increasing business returns and operational efficiency. An example of such can be the usage of serverless platforms for app deployment. You can also deploy your workload across a vast region so customers accessing it globally can experience quicker interaction.
Security
This fourth pillar focuses on protecting the confidential information, data, and systems of your business. It urges you to secure your applications by implementing strong identification protocols and access controls
Cost Optimization
The last focuses on optimizing and reducing the operational and up-front costs of cloud development for your business, along with a monitored and streamlined usage of resources. It recommends that you focus on core development activities while outsourcing all the ancillary services to a third-party vendor to reduce the time taken for development and corresponding costs.
To learn more about each pillar in detail, download our whitepaper here.
Cloud Security Governance Challenges
Following are some of the practical use cases of cloud governance strategies and how they help tackle governance challenges.
Safeguarding Against Eventualities
When a business avails cloud services from a vendor, it is the responsibility of the service provider to provide continuous and reliable services. It is also their responsibility to enhance said services. If the vendor’s service goes down, so will be the performance of the client. Having a proper cloud governance model in place helps avoid such situations.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cloud development is an extremely cost-effective approach to application making, and with the right governance policies in place, the business can reap huge profits. A well-optimized cloud governance model can run far more efficient financial analytics and yield an optimal way of automating these policies. It can also retain management reporting to help with cost management.
Data Security
Securing your data is one of the top priorities of any IT business, and a well-planned cloud strategy can secure you against hackers exploiting loopholes. Cloud governance policies and best practices dictate that you build a robust authenticating system to safeguard your confidential information. The reason behind such a strict rule is that cloud service providers such as AWS have many inherent security bugs.
At GoDgtl, we help businesses establish robust cloud governance frameworks for hybrid, cloud, and multi-cloud environments, enabling companies to maintain compliance, democratize data, and support collaboration.
Get in touch with our data modernization team to learn more about how we can help your company build a solid data governance framework.
Recent Posts
December, 2021





 The Benefits of Data Modernization
The Benefits of Data Modernization



