In today’s Digital Age, tremendous amounts of data are generated every single second from endless sources in various formats. First, there is structured data such as documents and spreadsheets, and now on the other side, there is unstructured data like emails, blog posts, videos, and even Twitter posts thrown into the vast mix of data. A recent study by Statista reveals that the total volume of data created, captured, and consumed globally reached 64.2 zettabytes in 2020. The study also predicts that by 2025, data creation worldwide is estimated to cross 180 zettabytes.
Every business organization in every shape and size all over the globe is pursuing digital transformation today. The generation of larger volumes of data together with global enterprises’ collective effort to transform themselves into digital businesses brings up storage challenges and the trouble of processing those myriad data types in vast volumes. Both these challenges put most business organizations under tremendous pressure to use a larger volume of data efficiently.
It is often legacy data architectures that stand in the way of nearly limitless opportunities to generate insights for effective business decision-making. Today’s massive surge in the volume, variety, and velocity of data baffles legacy databases, and they are bending under the heavyweight of these data challenges. Sooner or later, they may break. The only digital system that desperately needs modernizing is conventional on-premises data architecture. And the answer is data modernization.
What Is Data Modernization?
Data modernization includes extending yet retaining the value of legacy data assets, reusing the data buried in the layers of legacy databases, transforming them to updated modern data architectures, and correlating legacy data assets with the latest high-velocity data assets. It involves developing a scalable, flexible data stack, including modernizing databases without the limitations of many stages, integrations, and complexities. In other words, data modernization is simply moving data from legacy databases to modern databases. It is highly crucial for an enterprise that primarily deals with unstructured data.
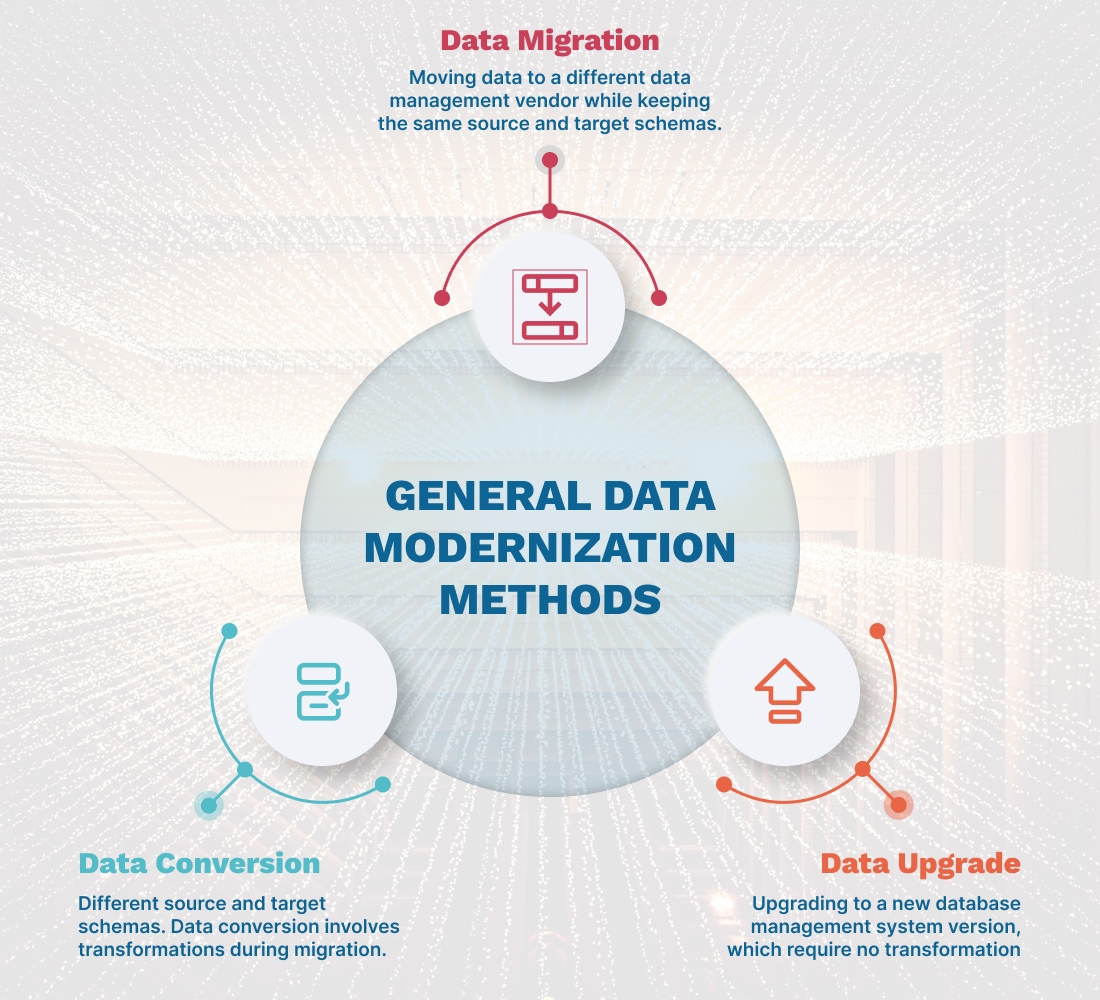
Three General Data Modernization Methods
Every business organization has its strategies and objectives. Therefore, data modernization doesn’t come with a one-size-fits-all size. Anyway, enterprises can implement three general data modernization methods depending on their business strategies and objectives.
Data Migration
This method involves moving data to a different data management vendor while the source and target schemas remain the same. Data migration includes migrating code, procedures, etc., which usually brings no significant changes to the application. In addition, an enterprise can utilize automation tools for complete data migration. For instance, moving the data from Sybase, a database management system (DBMS) vendor, to save licensing costs comes under data migration.
Data Conversion
The source and target schemas are different during this data modernization process. Data conversion involves transformations during migration. It is a typical data modernization method during re-engineering an application and modernizing a legacy application. Despite the availability of Extract Transform and Load (ETL) tools, the process is manual. For example, data movement from legacy databases like Indexed Sequential Access Method (ISAM) to Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) comes under data conversion.
Database Upgrade
This data modernization method involves upgrading to a newer version of the database management system, which requires no transformation. The deprecated code is replaced, and an enterprise can use automation tools to complete the upgrade. For instance, upgrading from SQL Server 2005 to SQL Server 2012 can be considered a data upgrade method.
 The Benefits of Data Modernization
The Benefits of Data Modernization
Here are some of the enterprise benefits of data modernization:
- It brings scalability to an enterprise to meet growing data analytics needs
- Efficient integration of new data sources to utilize data at any scale focusing on rising data volumes from multiple data sources
- Reduces the time to derive business insights. That means it provides the ability to find value in data even from streaming real-time data quickly.
- Democratize the process of data access for every business function
- Data modernization offers substantial cost benefits over traditional data management technologies.

Data modernization enables Information Technology (IT) enterprises and business leaders to attain and interpret data to anticipate market trends and improve business outcomes. As a result, a business acquires a solid competitive advantage by deriving actionable insights from enterprise data and data modernization strategies. It also allows organizations to deliver ideal Application Programming Interface (API)-driven application integrations and prompt decision-making in a dynamic business ecosystem.
Recent Posts
Let's Talk
Our GoDgtl team is ready to help you!
We appreciate your interest in GoDgtl. Please select which team of experts you wish to engage:
 The Benefits of Data Modernization
The Benefits of Data Modernization